3.6.1 User Management #
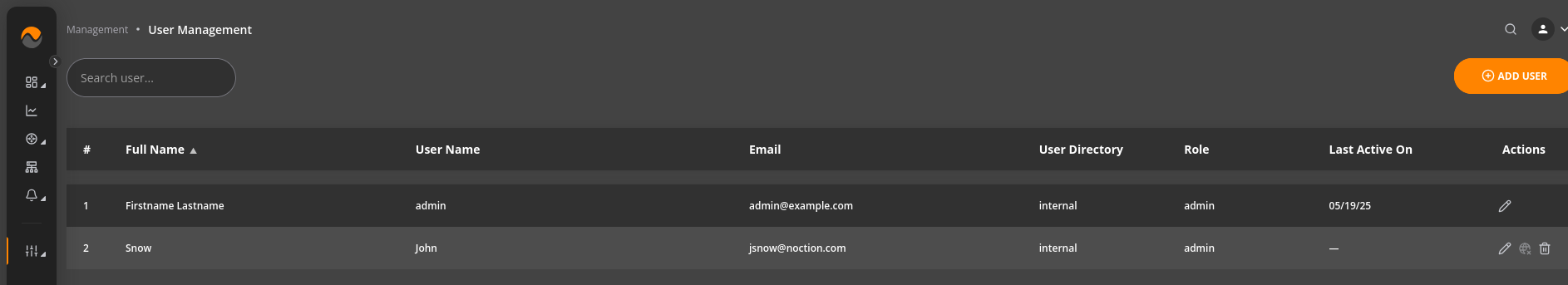
NFA includes a User Management function accessible under Management main menu section,
that allows the following:
- review and filter the list of users
- edit and delete existing user records
- add new users
3.6.2 LDAP user directories #
LDAP user directories can be added, updated and removed from NFA by accessing Management > User Management. Each user directory takes a series of parameters specific for the protocol.
All operations with DNs (initial bind DN, group DNs, user names) are case insensitive and also strip redundant whitespace.
Refer to individual protocol documentation for how to correctly configure one or another user directory.
The example below offers a generic set of parameters required to configure NFA to use Active Directory for access management.
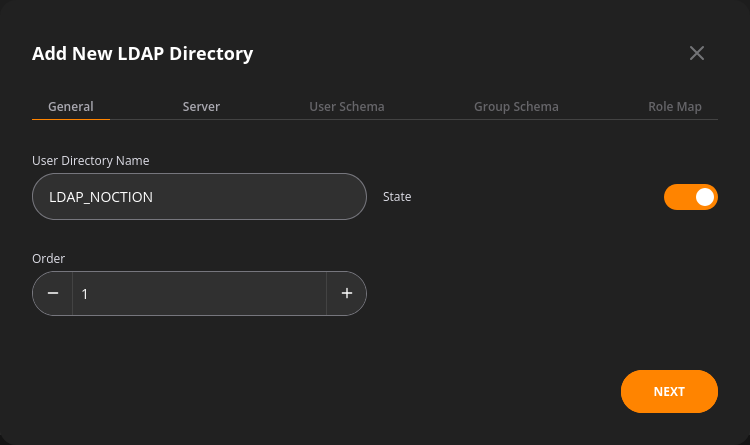
The general tab covers:
- User directory name – the name assigned to the directory within NFA
- User directory type
- State – a toggle to enable or disable a user directory,
- Order specifies when this user directory will be examined by NFA compared to other user directories
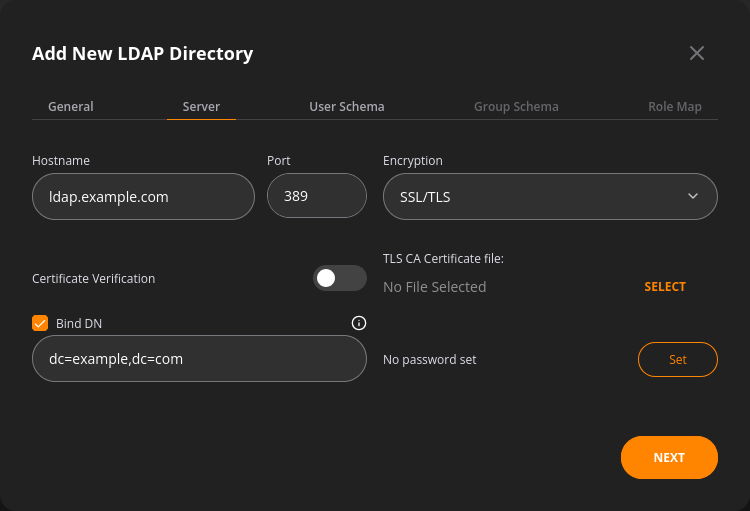
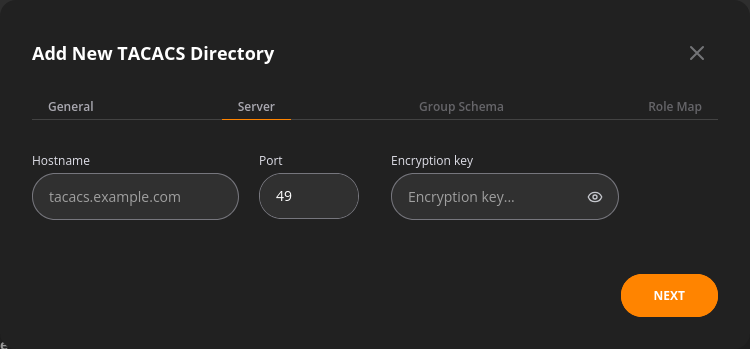
The server tab covers:
- User directory hostname in the form of either IP address or domain name (LDAP/LDAPS)
- User directory port
- SSL, TLS, or no encryption selector
- Certificate verification toggle and TLS CA Certificate file options in case the TLS encryption is selected
- The binding user name that NFA uses to authenticate itself
- Bind password assigned to NFA
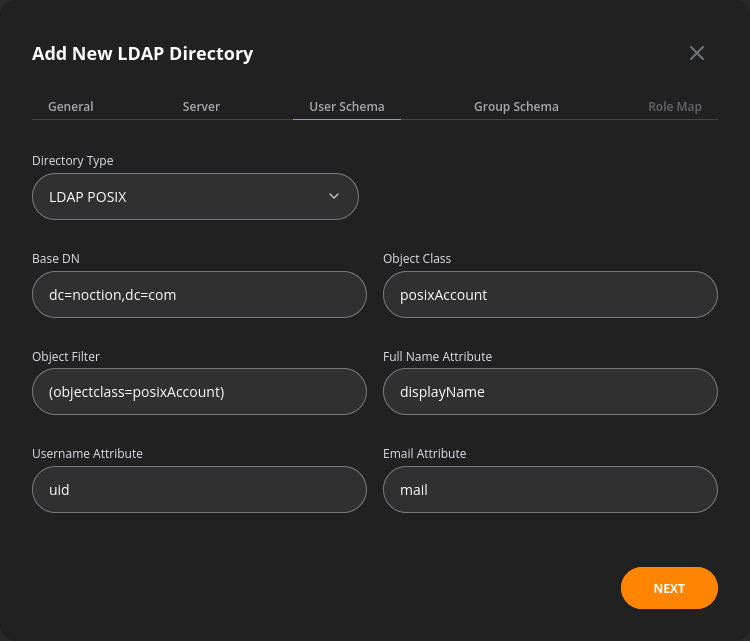
The user schema tab covers:
- The Generic, LDAP POSIX, or Active Directory type selector
- Base DN specifies the root distinguished name and user subtree
- Object Class – an attribute that defines the characteristics of an object in the directory
- Object Filter – a search criterion used to find objects in the directory that match a specific set of attributes
- Username, Email, and Full Name fields map the User Directory attributes to NFA user attributes
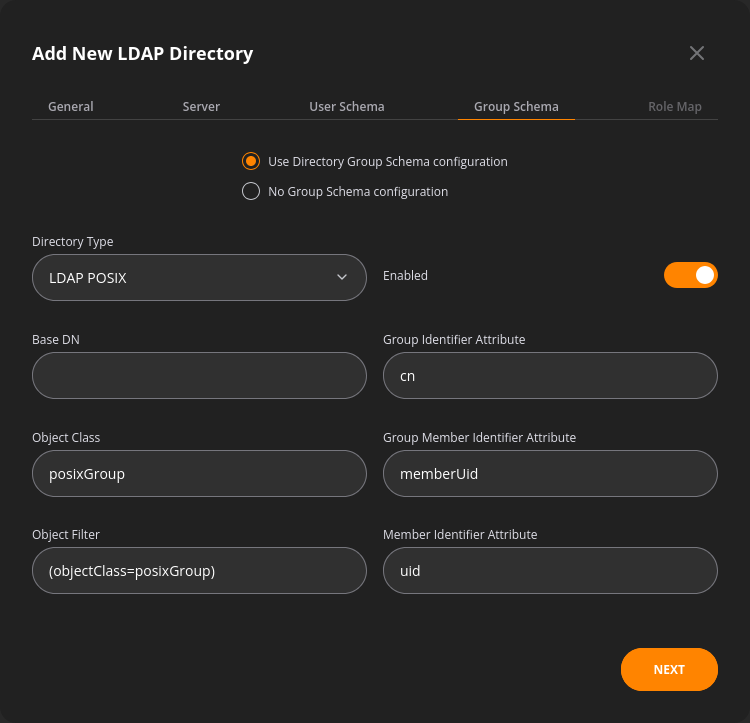
The group schema tab covers:
- The Generic, LDAP POSIX, or Active Directory type selector
- Base DN specifies the root distinguished name and user subtree
- Object Class – an attribute that defines the characteristics of an object in the directory
- Object Filter – a search criterion used to find objects in the directory that match a specific set of attributes
- Group Identifier, Group Member Identifier, Member Identifier fields map the User Directory attributes to NFA user attributes
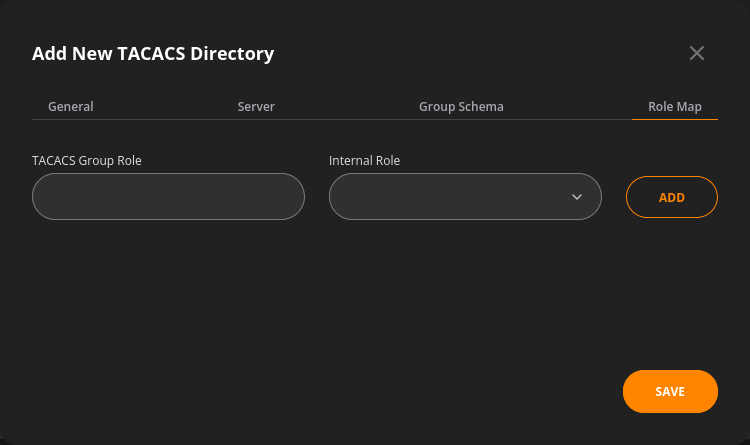
3.6.3 TACACS+ user directories #
TACACS+ user directories can be added, updated and removed from NFA by accessing Management > User Management. User directory takes a series of parameters specific for the protocol.
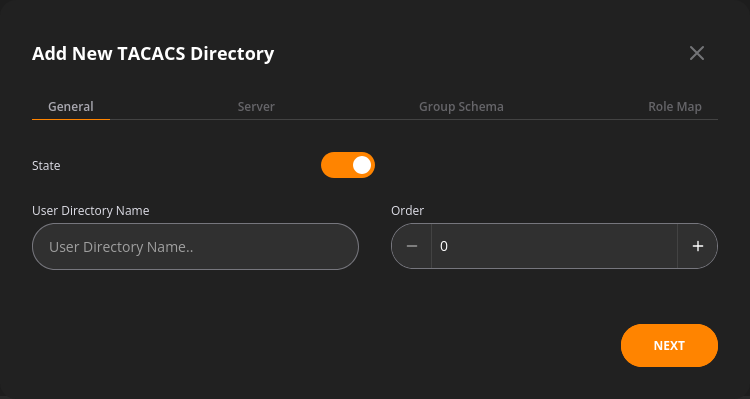
The general tab covers:
- User directory name – the name assigned to the directory within NFA
- State – a toggle to enable or disable a user directory,
- Order specifies when this user directory will be examined by NFA compared to other user directories
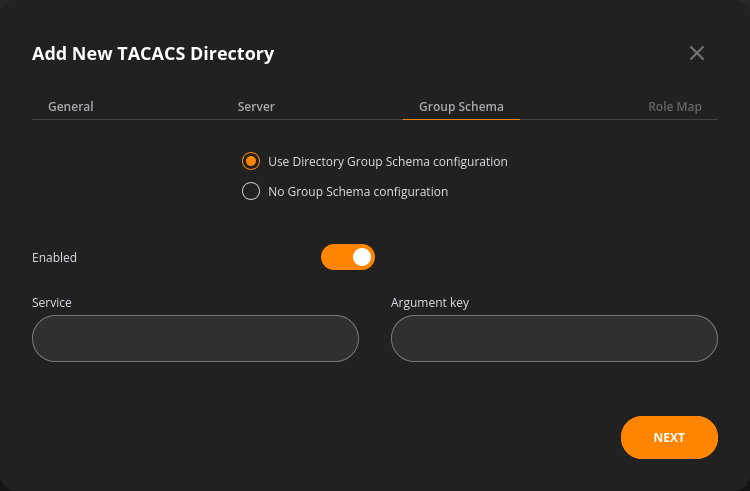
The group schema tab covers:
- The Service parameter
- The Argument Key
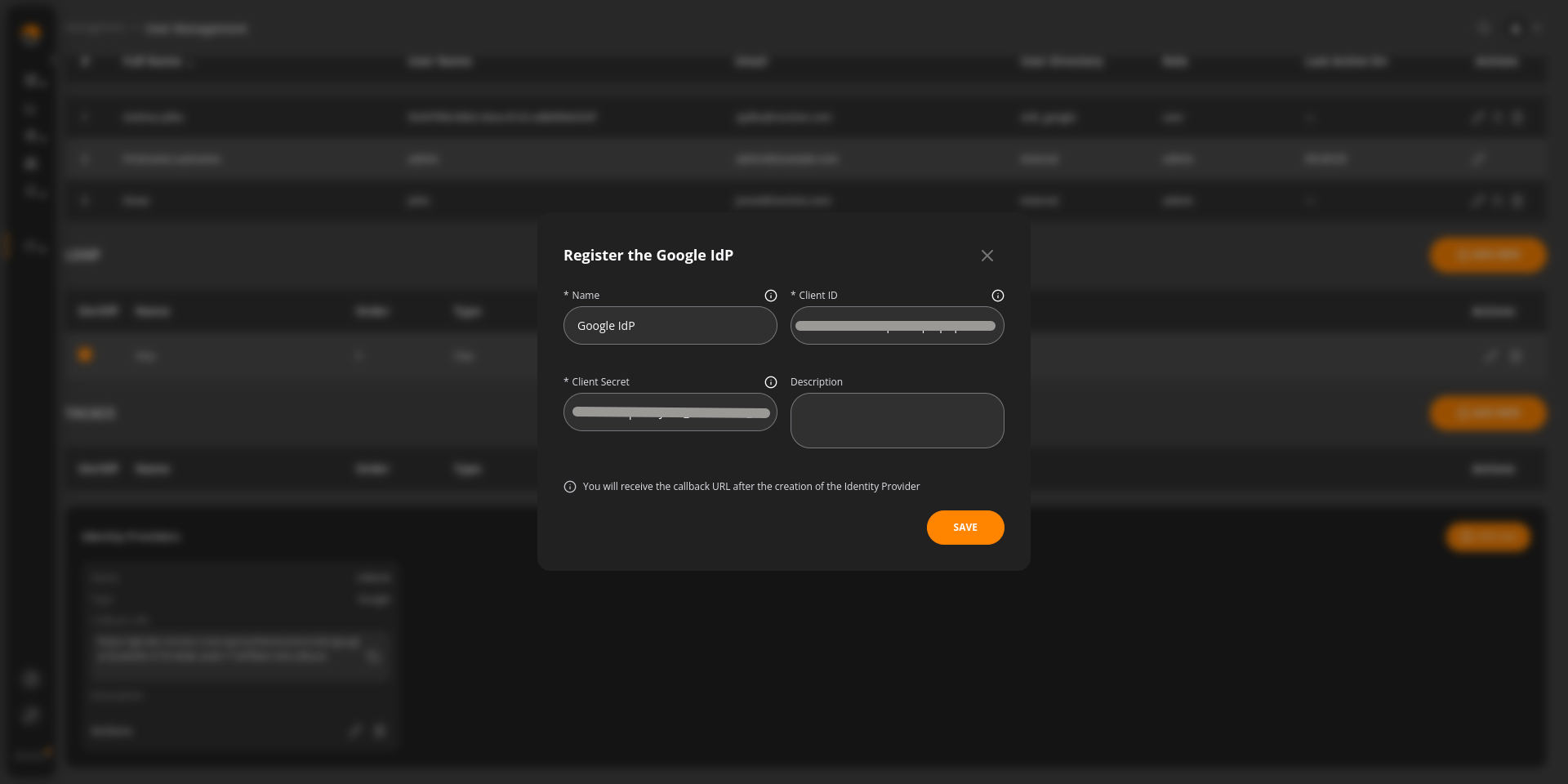
3.6.4 Google OIDC #
Google OIDC (OpenID Connect) authentication provides a standardized method for users to log in to an application using their Google account.
How it works in NFA:
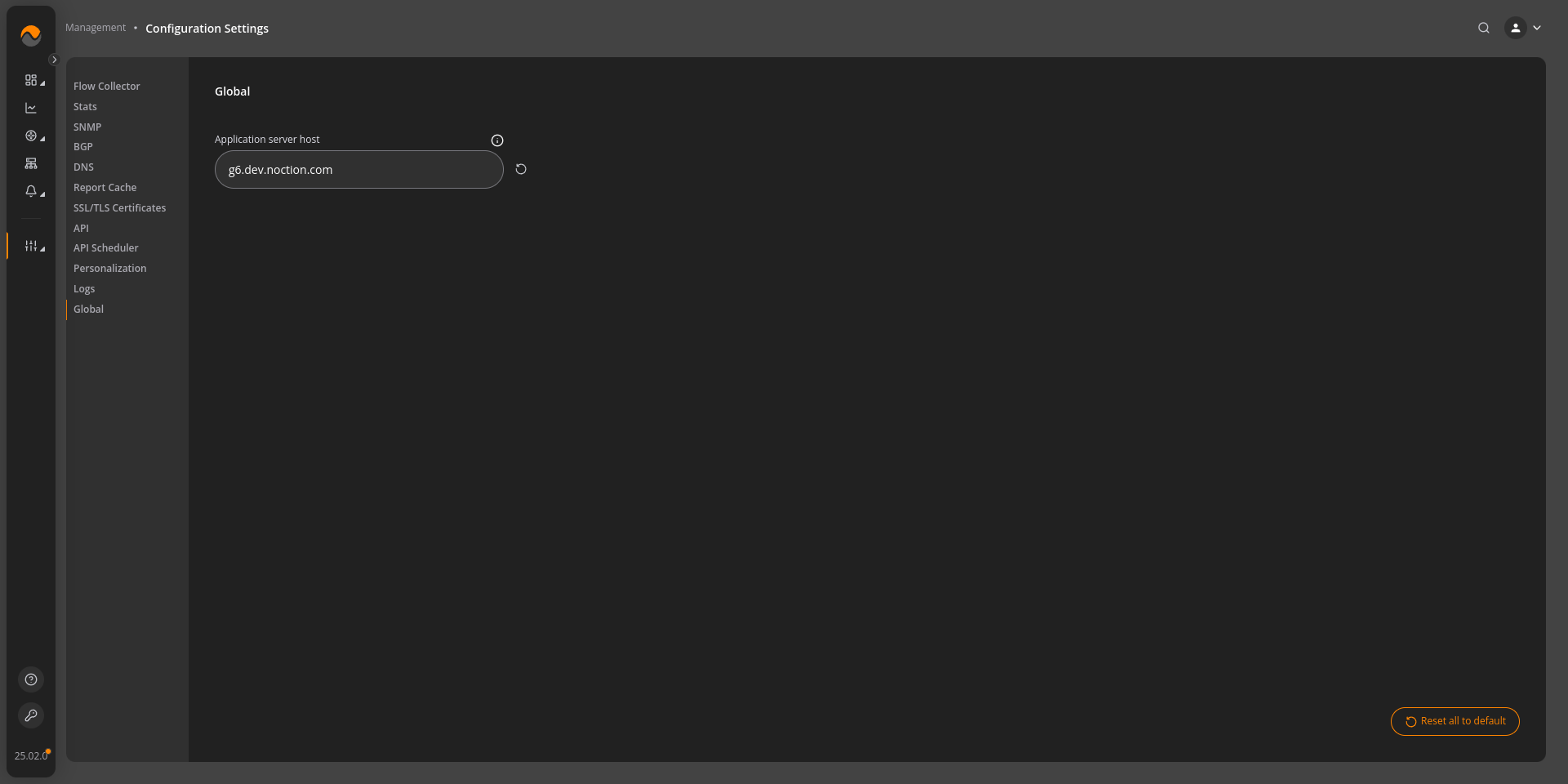
Set the Application Server Host
Navigate to Management → Configuration Settings → Global, and configure the application server host.
Create an OAuth2 Client in Google Developers Console.
Go to the Google Developers Console. Create a new OAuth 2.0 Client ID. After creation, you’ll receive a Client ID and Client Secret.
Configure Identity Provider in NFA
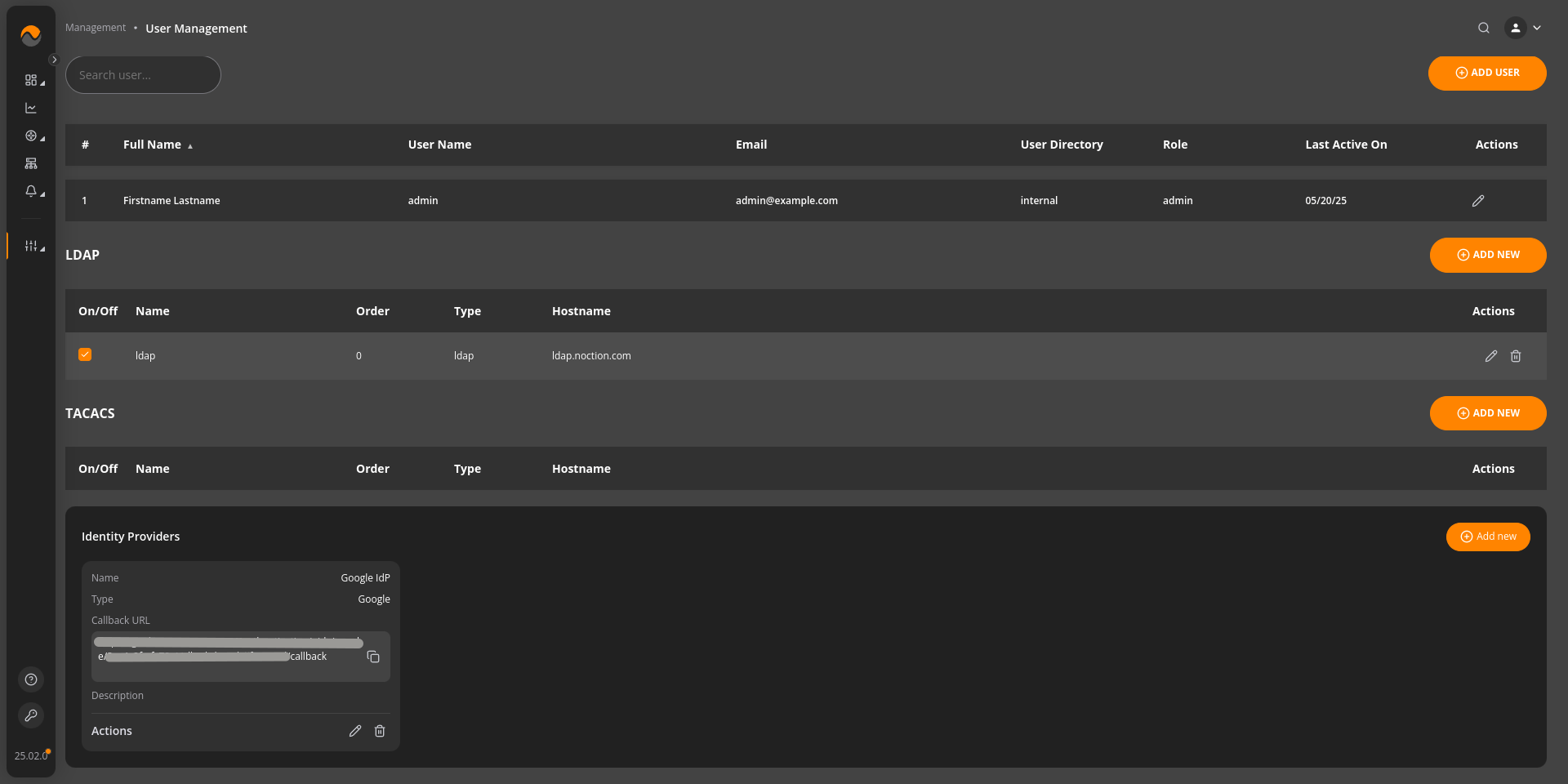
Go to Management → User Management. Click on “Add New Identity Provider”.
Enter the Client ID and Client Secret you received from the Google Developers Console.
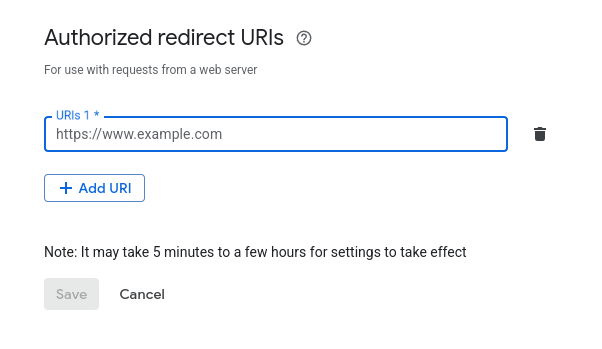
Set Up Redirect URI
The callback URI will be shown in the frontend after adding the identity provider.
Copy this URI and add it to the Authorized Redirect URIs section in the Google Developers Console.
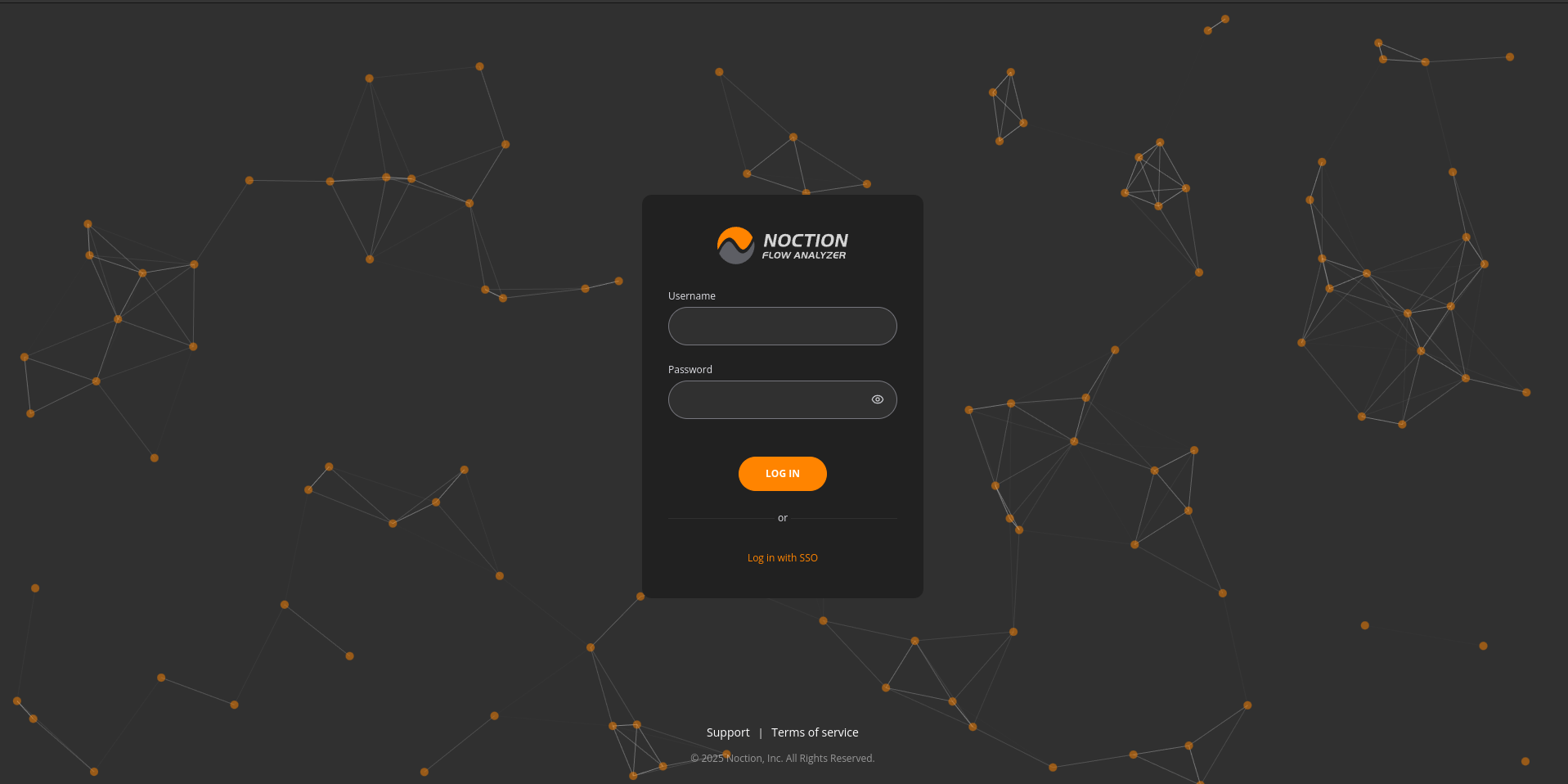
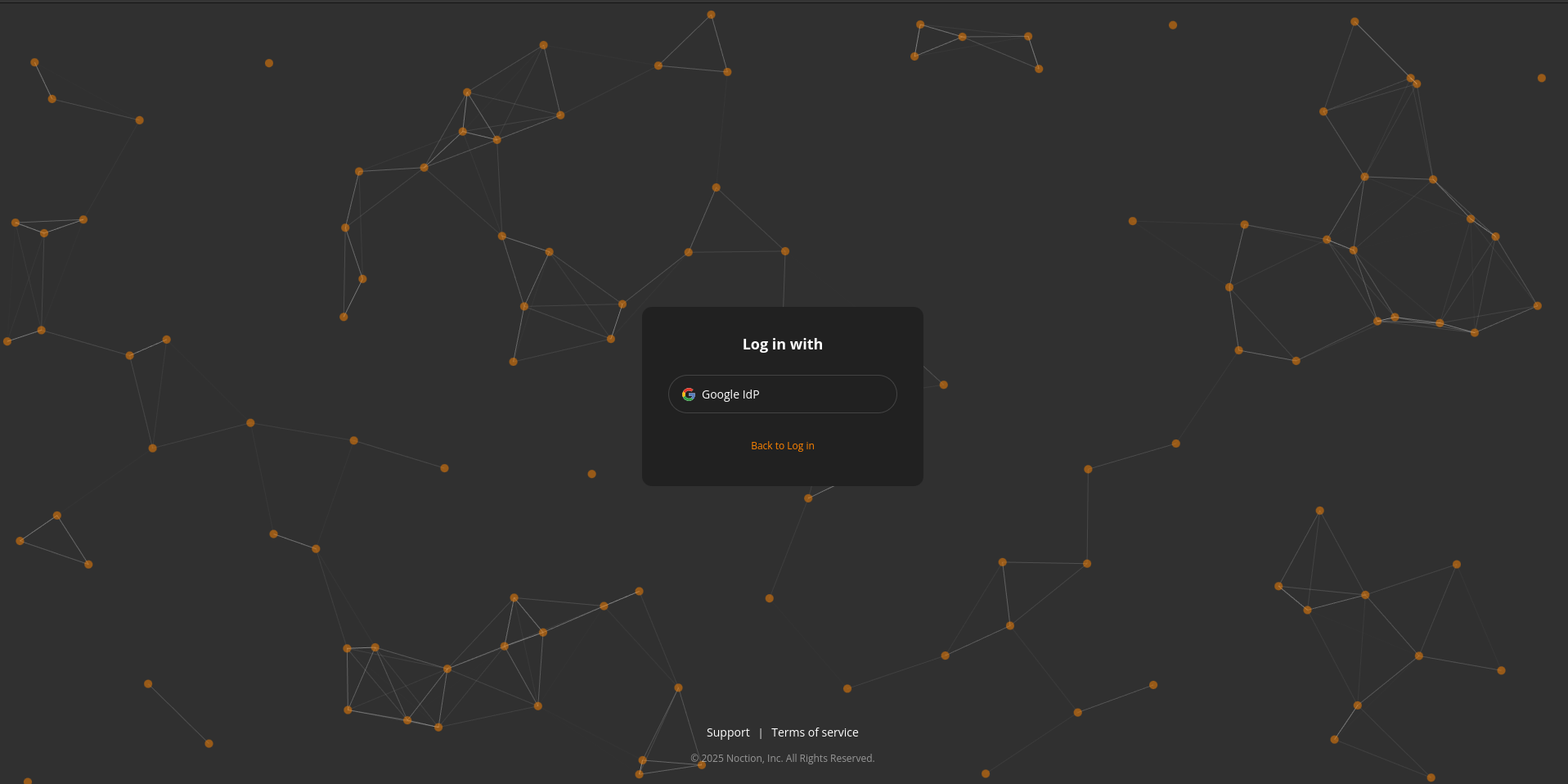
Log In Using SSO
Click SSO login.
3.6.5 Radius #
RADIUS (Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service) is a network protocol and service used to provide:
Authentication – Verifying a user’s identity.
Authorization – Determining what resources the user is allowed to access.
How to use Radius in NFA:
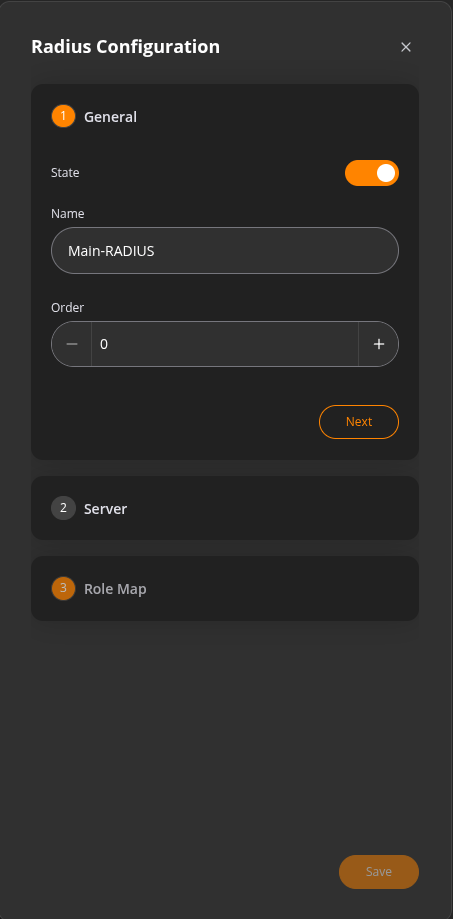
Step1:
Provide the following details:
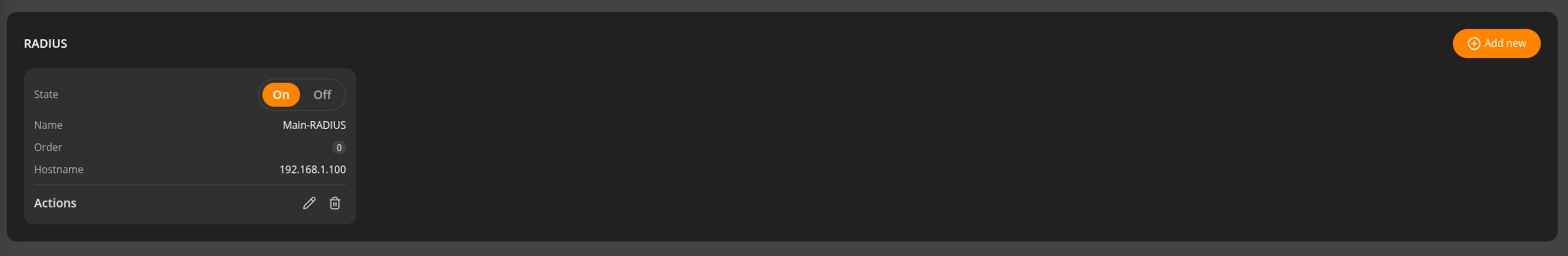
- State – Enable or disable the RADIUS service.
- Name – A friendly name for the RADIUS server (for easy identification).
- Order – The priority or order in which this server should be used, in case multiple RADIUS servers are configured.
 Step2:
Step2:
Provide the following details:
Hostname
The server’s address (either an IP or fully‑qualified domain name).- Port
The UDP port RADIUS listens on (default: 1812 for authentication).
- Timeout
How long (in seconds) the client should wait for a response before retrying.
- Secret Key
The shared secret used to encrypt and validate messages (write‑only; you won’t be able to read it back once saved).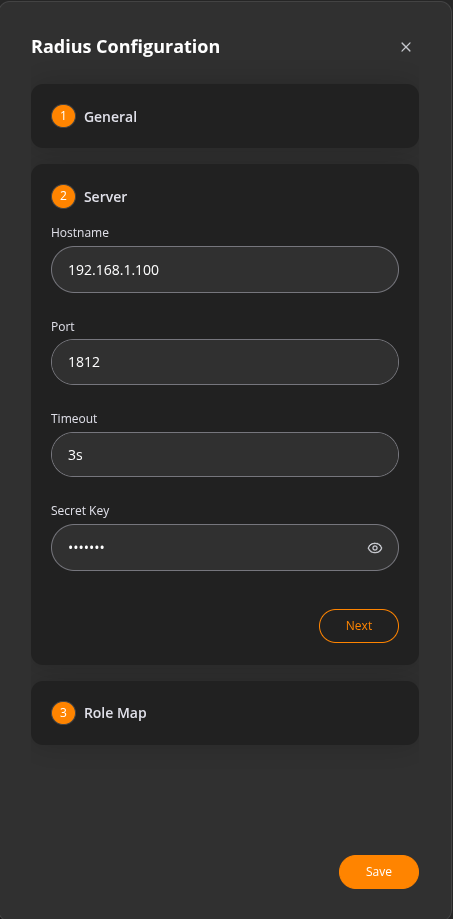 Step3:
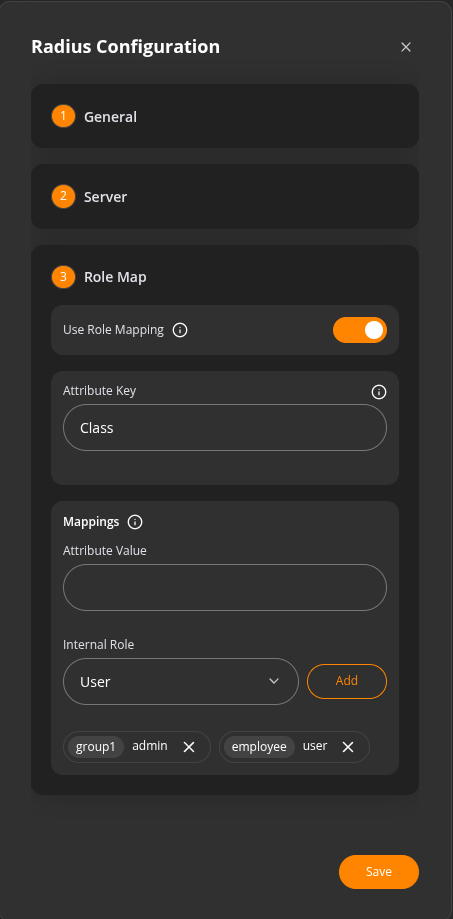
Step3:
In this step, you define how users are assigned roles based on attributes received from the RADIUS server. You need to provide:
You can add one or more RADIUS services. Each service can be edited or deleted as needed.
- Port